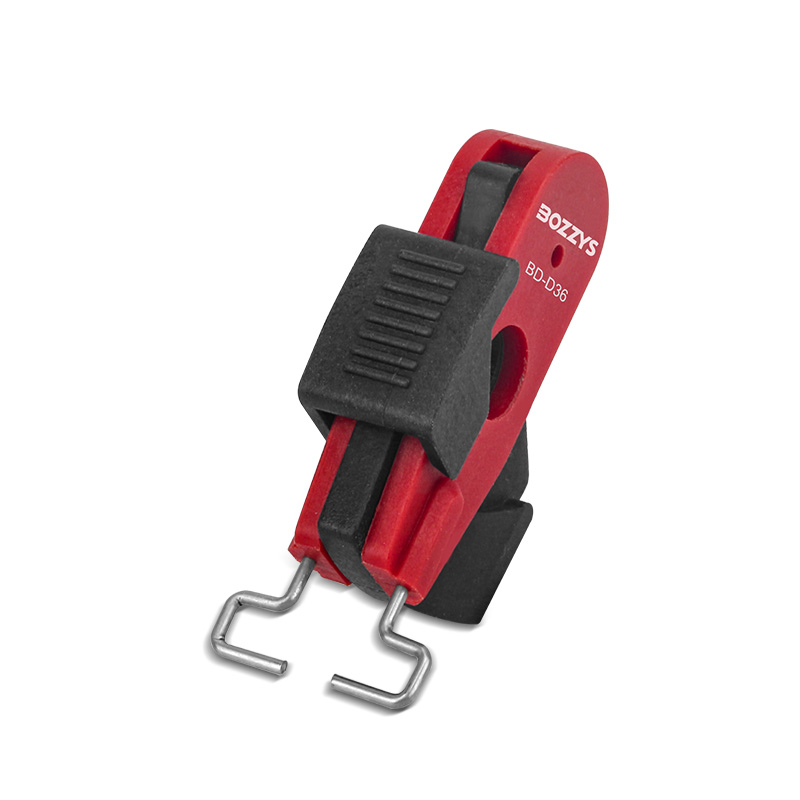
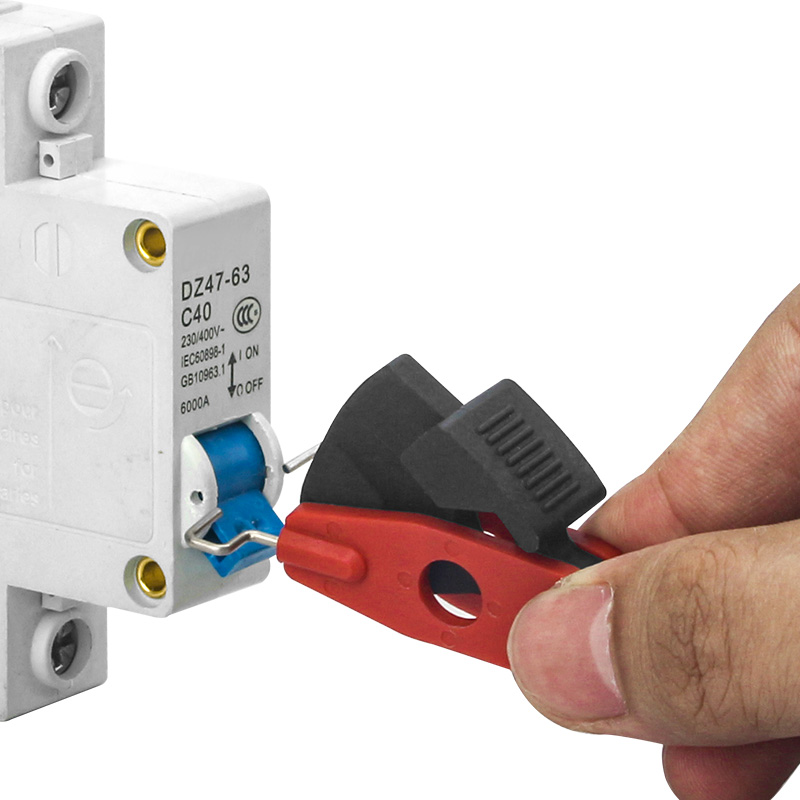
Electrical lockouts are vital safety measures used to protect workers from dangerous electrical hazards. When electrical equipment needs repair or maintenance, it must be turned off and secured to prevent accidental startup. This is where electrical lockouts come in. They are special devices that physically block switches and controls, making sure the equipment stays off while work is being done. These lockouts often include tags with warnings and information about who is working on the equipment. Using lockouts is a key part of workplace safety rules in many industries. They help prevent serious accidents like electric shocks or injuries from machines suddenly turning on. Proper use of electrical lockouts involves a step-by-step process that workers must follow carefully. This includes identifying all power sources, shutting them off, testing to make sure no power remains, and then applying the lockout devices. Only when the work is finished and everyone is clear can the lockouts be removed and the equipment turned back on. By using electrical lockouts correctly, companies can greatly reduce risks and keep their workers safe.
Functions of electrical lockouts
Isolation of Energy Sources
Electrical lockouts physically disconnect equipment from power sources. They’re placed on switches, circuit breakers, or plugs to keep them in the “off” position. This creates a barrier between workers and live electrical parts, reducing the risk of electrocution or unexpected machine startups. The lockout devices come in various forms, like padlocks, tags, or specialized covers, depending on the type of equipment. They’re designed to be sturdy and tamper-resistant, ensuring that power can’t be restored accidentally. This isolation is the first and most crucial step in making equipment safe for maintenance or repair. It’s not just about flipping a switch; lockouts provide a physical, visible barrier that everyone can see and understand, making the work area much safer for all involved.
Visual Warning
Lockout devices serve as clear visual warnings. They’re often brightly colored, usually red or yellow, and impossible to miss. When workers see a lockout in place, they immediately know that the equipment is being serviced and should not be used. This visual cue helps prevent accidents caused by someone unknowingly trying to operate locked-out equipment. It’s a simple but effective way to communicate danger and ongoing work. The presence of a lockout device also reminds other workers to stay alert and cautious around the area. Even from a distance, these visual signals can quickly convey important safety information. This function is particularly useful in busy or noisy work environments where verbal warnings might be missed or forgotten.
Personal Safety Assurance
Each worker involved in the maintenance or repair can attach their own personal lock to the lockout device. This means the equipment can’t be turned on unless every single lock is removed. It gives each worker control over their own safety. They know the machine can’t start up while their lock is in place, even if others finish their tasks. This personal control is a key feature of lockout systems. It empowers workers to take charge of their safety and not rely solely on others. If a worker needs to leave the area temporarily, their lock ensures the equipment stays off until they return. This individual accountability helps create a strong safety culture and reduces the risk of miscommunication or oversight.
Documentation and Communication
Lockout tags attached to the devices provide important information. They typically include the name of the person who applied the lock, the date, and the reason for the lockout. This creates a clear record of who is working on what and why. It helps with communication between shifts and ensures everyone knows the status of the equipment. Good documentation is crucial for safety and helps manage complex repair or maintenance projects. These tags can also include contact information, expected completion times, or special instructions. In large facilities or for long-term projects, this documentation helps coordinate work across teams and departments. It creates a paper trail for safety audits and can be valuable for troubleshooting recurring issues.
Compliance with Safety Regulations
Using electrical lockouts helps companies follow safety laws and industry standards. Many countries have strict rules about protecting workers from electrical hazards. By using proper lockout procedures, businesses show they are taking these rules seriously. This can help avoid fines and legal problems. More importantly, it shows a commitment to worker safety and helps create a culture of safety in the workplace. Compliance often requires training programs for workers, regular audits of lockout procedures, and maintaining records of lockout use. While it might seem like extra work, these practices ultimately save time and money by preventing accidents. They also improve a company’s reputation and can lead to better insurance rates.
Prevention of Accidental Re-energization
Lockouts physically prevent equipment from being turned back on by mistake. Even if someone flips a switch or presses a start button, the lockout device keeps the power off. This is crucial because accidental startups are a major cause of workplace injuries. The physical barrier provided by lockouts adds an extra layer of protection beyond just turning things off or unplugging them. It guards against various scenarios, like automatic power restoration after an outage, or well-meaning but uninformed coworkers trying to “help” by turning equipment back on. This function is especially important in complex systems where power sources might not be obvious, or in situations where multiple people or teams are working on interconnected equipment.
Enabling Safe Maintenance and Repair
By ensuring equipment stays de-energized, lockouts create a safe environment for maintenance and repair work. Technicians can work on electrical systems, moving parts, or other potentially dangerous areas without fear of sudden power restoration. This allows for more thorough and careful work, improving the quality of repairs and maintenance. It also reduces stress on workers, knowing they are protected from unexpected hazards while they focus on their tasks. Safe conditions lead to better concentration and fewer mistakes. Additionally, when workers feel secure, they’re more likely to report potential issues or suggest improvements, contributing to overall workplace safety and efficiency. The peace of mind provided by proper lockout procedures can significantly enhance both the safety and effectiveness of maintenance operations.
Conclusion
Electrical lockouts are essential tools for workplace safety, especially when dealing with electrical equipment. They protect workers from dangerous accidents by keeping machines turned off during maintenance or repairs. Lockouts provide clear visual warnings, allow personal control over safety, and help with communication between workers. They also ensure companies follow safety rules and prevent accidental start-ups.
By creating a safe environment for maintenance, lockouts improve the quality of work and reduce stress on workers. While they may seem like a small step, electrical lockouts play a big role in preventing injuries and saving lives. Proper use of lockouts shows a strong commitment to safety and helps build a culture where everyone looks out for each other’s well-being.


 2
2